2004 FH SCHEERDE LANGS DE AARDE

Klik op de afbeelding voor een 2 Mb filmpje van de scheervlucht van
2004 FH op 18 maart.
Opnamen: Stefano Sposetti, Zwitserland. Animatie: Raoul Behrend, Geneva Observatory, Zwitserland.

Klik op de afbeelding voor een 2 Mb filmpje van de scheervlucht van
2004 FH op 18 maart.
Opnamen: Stefano Sposetti, Zwitserland. Animatie: Raoul Behrend, Geneva Observatory, Zwitserland.
18 maart 2004, 08.30 u.
Minder dan 24 uur geleden werd een planeto´de ontdekt die rakelings langs de aarde zal scheren. 'Rakelings' is hier weliswaar 49.000 km vanaf het centrum van de aarde (43.000 km boven het oppervlak van de aarde), maar dat is slechst een achtste van de afstand aarde-maan. Gelukkig is 2004 FH 'maar' 30 meter in diameter. De aarde kruipt weer eens door het oog van de naald...
Carl Koppeschaar
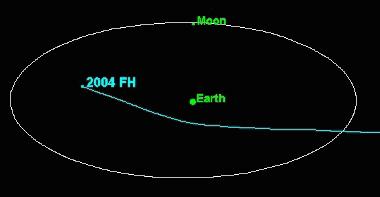
Door de zwaartekrachtswerking van de aarde zal planeto´de 2004 FH vandaag
15o van zijn oorspronkelijke baan worden afgebogen.
This Is SKY & TELESCOPE's AstroAlert for Minor Planets
March 18, 2004
CLOSEST FLYBY EVER
Less than 24 hours from the time this message is being issued, a tiny,
newly discovered asteroid will make the closest flyby past Earth that has ever
been predicted by astronomers.
The object, dubbed 2004 FH, is probably only about 20 meters in diameter (the size of a house). An electronic circular issued late on March 17th by the Minor Planet Center i n Cambridge, Massachusetts, indicates that it will definitely not hit the Earth. It will pass about 49,000 kilometers (30,500 miles) from Earth's center, which is one-eighth the distance of the Moon.
This object was discovered on March 16th by astronomers of MIT's Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research (LINEAR) survey in Socorro, New Mexico. Further observations made on the 17th at Klet Observatory (Czech Republic), Starkenburg Observatory (Germany), and Modra Observatory (Slovenia) helped the Minor Planet Center compute its exact trajectory.
The flyby scenario for 2004 FH goes like this:
Because 2004 FH will be passing so close, it is not practical for me to include a detailed ephemeris in this message. Its path across the sky depends greatly on an observer's vantage point on Earth (owing to the parallax effect). Observers who wish to locate it in small telescopes should use the Minor Planet Center's Ephemeris Service to make detailed predictions for their own geographic location.
According to the orbit calculated by Gareth Williams, associate director of the Minor Planet Center, 2004 FH belongs to the Aten class of asteroids. It circles the Sun in just under 9 months in very nearly the same plane as Earth's orbit. At perihelion it swings well inside the orbit of Venus; at aphelion (as currently) it ranges just outside that of the Earth.
Roger W. Sinnott
Senior Editor
SKY & TELESCOPE
 Back to ASTRONET's home page
Back to ASTRONET's home page
 Terug naar ASTRONET's home page
Terug naar ASTRONET's home page